By Yishane Lee
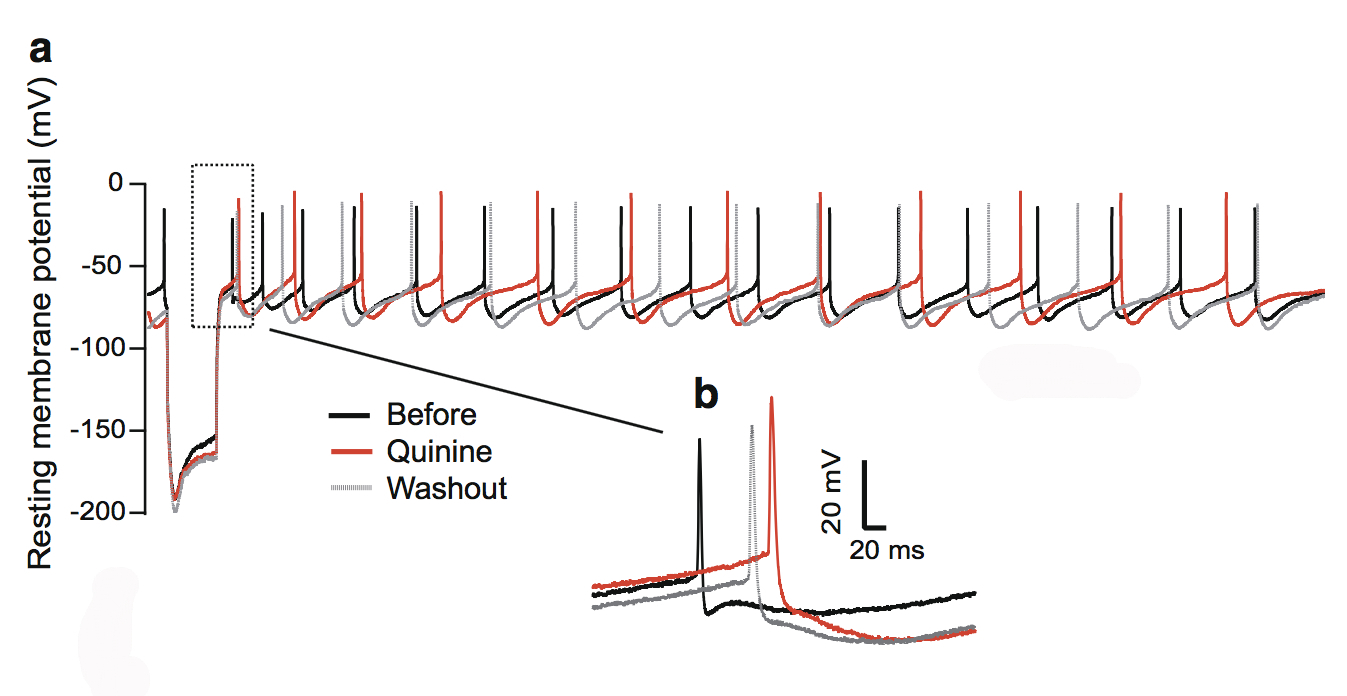
Recent genetic studies have identified that the protein Ripor2 (formerly known as Fam65b) is an important molecule for hearing. It localizes to the stereocilia of auditory hair cells and causes deafness when mutations disrupt its function.
In a study published in the Journal of Molecular Medicine in November 2018, Oscar Diaz-Horta, Ph.D., a 2017 Emerging Research Grants (ERG) scientist, and colleagues further show the role the protein plays by demonstrating how it interacts with other proteins during the development of the hair cell bundle. The team found that the absence of Ripor2 changes the orientation of the hair cell bundle, which in turn affects hearing ability.
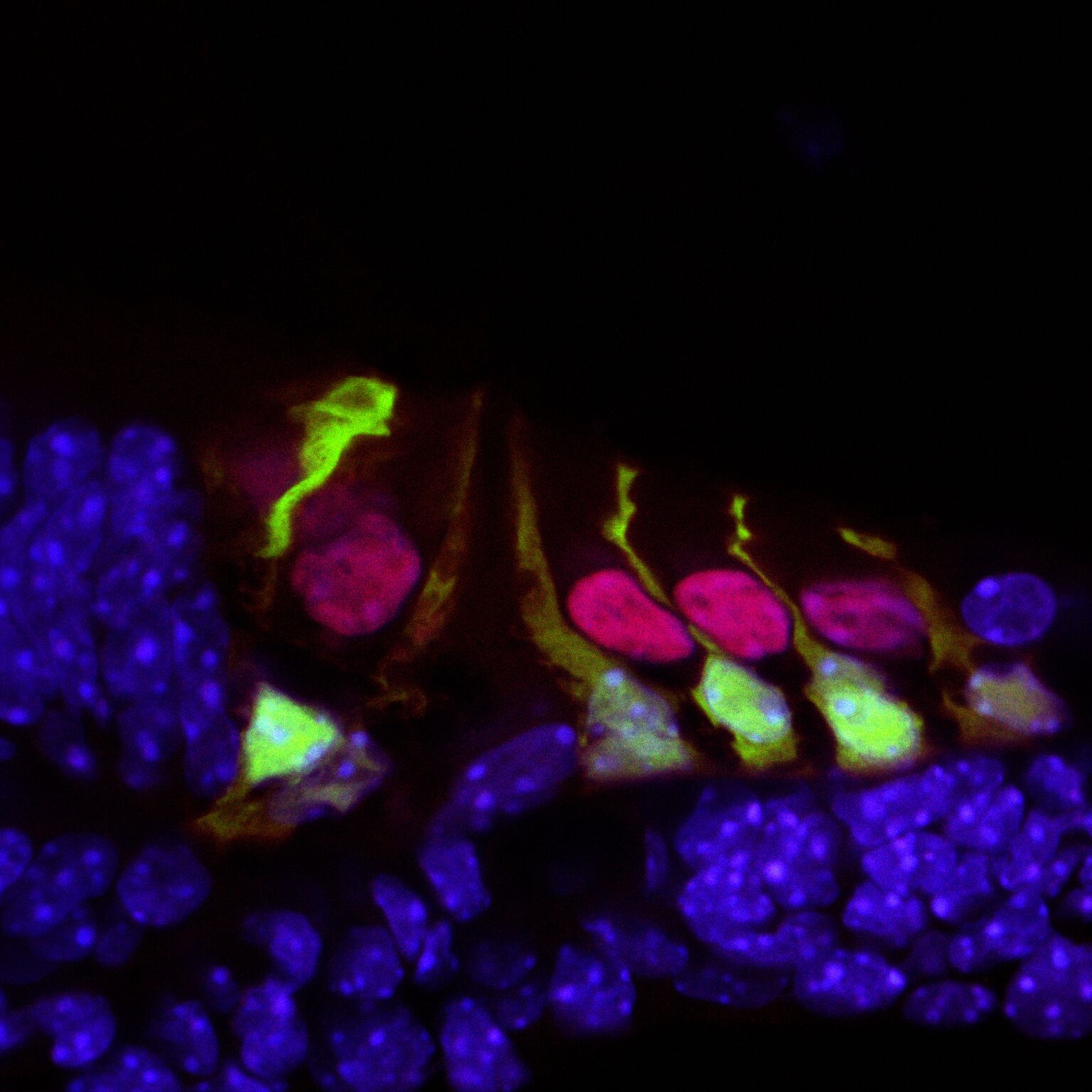
Ripor2 interacts with Myh9, a protein encoded by a known deafness gene, and Myh9 is expressed in the hair cell bundle stereocilia as well as its kinocilia (apices). The team found that the absence of Ripor2 means that Myh9 is low in abundance. In the study, Ripor2-deficient mice developed hair cell bundles with atypically localized kinocilia and reduced abundance of a phosphorylated form of Myh9. (Phosphorylation is a cellular process critical for protein function.)
Another specific kinociliary protein, acetylated alpha tubulin, helps stabilize cell structures. The researchers found it is also reduced in the absence of Ripor2.
The study concludes that Ripor2 deficiency affects the abundance and/or role of proteins in stereocilia and kinocilia, which negatively affects the structure and function of the auditory hair cell bundle. These newly detailed molecular aspects of hearing will help to better understand how, when these molecular actions are disrupted, hearing loss occurs.
A 2017 ERG scientist funded by the Children’s Hearing Institute (CHI), Oscar Diaz-Horta, Ph.D., was an assistant scientist in the department of human genetics at the University of Miami. He passed away suddenly in August 2018, while this paper was in production. HHF and CHI both send our deepest condolences to Diaz-Horta’s family and colleagues.
We need your help supporting innovative hearing and balance science through our Emerging Research Grants program. Please make a contribution today.