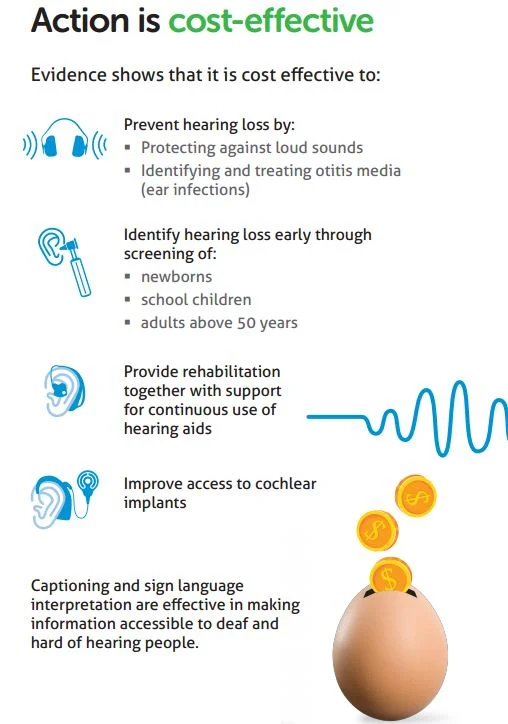
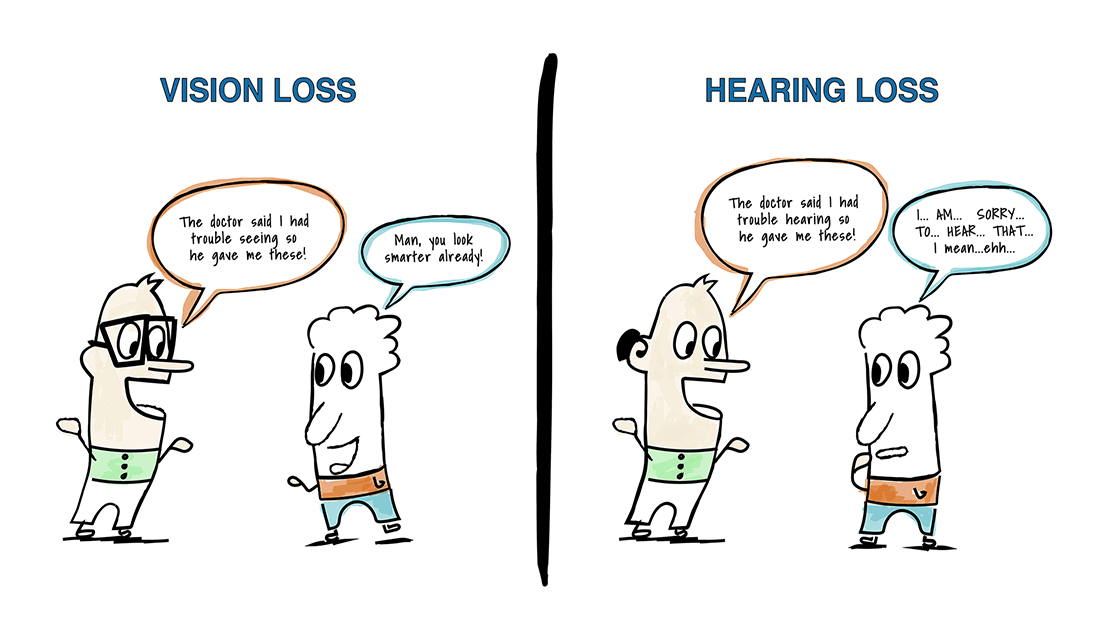
Hearing loss is frequently associated with older folks. When we think of younger people and teens as being deaf or hard of hearing, we tend to assume they have been that way since birth. But that’s not always the case; children and teens can lose their hearing just as older people can, sometimes quite suddenly.
It is important to understand not only the causes of hearing loss, but also the serious issues that result. Hearing loss affects social interaction and emotional well-being, and only by appreciating these effects can friends, teachers, parents and other support figures help teens navigate the troubled times ahead. The below blog post discusses more root causes and the importance hearing has on our society.
What causes hearing loss in teens?
Hearing loss in teens can result from many factors, including congenital defects, ear infections, autoimmune diseases, blows to the head or exposure to loud noises. This is not a complete list, unfortunately; hearing loss can result from many other issues besides.1
Understanding levels of hearing loss
While we tend to think of people as either hearing or deaf, hearing is not an absolute sense. Rather, it exists on a scale.2 So while some teens may have no hearing ability whatsoever, others may have some. When hearing begins to fade, people first have trouble picking up softer noises, then louder ones. Teens may first lose their ability to hear low hums and birds chirping and then lose spoken words in a vacuum. Eventually, in full hearing loss, they cannot hear even loud noises such as helicopters or gunshots.
The cultural importance of hearing
Sadly, hearing is not only a valuable means of communication; it is also fraught with cultural importance. Not being able to hear causes teens to miss many social cues that other, hearing, teens rely on.
For instance, they may miss the physical characteristics of voice, different dialects, varying speech registers (the ways we speak in informal versus formal situations, or at work versus at home), and the internal or emotional states of the people around them.3 These are all crucial pieces of cultural information to which the deaf and hard of hearing do not have access.
Learning impacts of deafness from birth
Deafness from birth, especially when it comes to deaf teens born to hearing parents, comes with a price tag not attached to deaf teens born to deaf parents or hearing teens who later become deaf.4 This is because when children are able to interact with parents on a daily basis during their formative years – hearing children with hearing parents or deaf children with deaf parents – they benefit from crucial language interaction.
However, teens who were born deaf to hearing parents often suffer from a disconnect that results from being unable to communicate easily. Reading levels, memory, emotional adjustment and other aspects of life may suffer.
Emotional, social and educational results of hearing loss
Even if children are able to skip the often negative effects of early deafness, hearing loss of any type has huge impacts socially, emotionally and educationally.
Teens who experience hearing loss and can’t compensate for its effects often respond in typical ways: becoming confused, checking out, losing self-reliance, feeling isolated and losing their identity.5 This impacts their ability to engage in school, to form peer relationships, to be close to their families and to pursue their interests. Such issues can be hard to overcome, but with good communication, it’s possible.
Tips for communicating with the deaf and hard of hearing
It can be quite difficult to learn to communicate with deaf or hard of hearing teens if you have never learned sign language, especially if the onset of hearing loss is sudden. However, there are a number of steps that you can take to make communication easier.
Remember, hard-of-hearing teens will rely heavily on your facial and mouth movements, so give them a full view of your face, avoiding moving or fidgeting. Don’t exaggerate your words, because this distorts how you form them, and supplement the conversation with bodily and facial gestures as you normally would.6
Mitigating the psychological effects of teen hearing loss
Helping teens foster a sense of self that moves past the disability is important, as is helping them to establish an understanding community. Supporting their efforts to communicate is crucial, but offering space where needed is very important as well. Overall, it will take time and effort – on the teen’s part and on the part of his or her support team – to overcome the disability and learn to lead a full and natural life once more. But with understanding, love and help, teens can get there.
Ann Steele, Psy.D., LMFT is the author and publisher of the "Psychology Effects of Hearing Loss in Teens."
Hearing Loss Association of America (2016). Types, Causes and Treatment. Retrieved from http://www.hearingloss.org/content/types-causes-and-treatment.
World Health Organization (2016). Grades of Hearing Impairment. Retrieved from http://www.who.int/pbd/deafness/hearing_impairment_grades/en/.
Krauss, Robert M., & Pardo, Jennifer S. (2006). Speaker Perception and Social Behavior: Bridging Social Psychology and Speech Science. Retrieved from http://www.columbia.edu/~rmk7/PDF/Bridges.pdf.
Henderson, Valerie, Grinter, Rebecca E., & Starner, Thad (2005). Electronic Communication by Deaf Teenagers. Retrieved from https://smartech.gatech.edu/bitstream/handle/1853/8451/05-34.pdf.
Better Hearing Institute (2016). Consequences of Hearing Loss. Retrieved from http://www.betterhearing.org/hearingpedia/consequences-hearing-loss.
South Carolina Hospital Association. Tips for Communicating with Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing People. Retrieved from http://www.scha.org/files/documents/tips_for_communicating_with_deaf_and_hard.pdf.